RAID 0 operating principle: striping
The RAID 0 system is based on the clustering of at least two hard disks, ideally of the same size and model. The data stored on these disks is distributed instripes across all the disks in the system. This storage architecture, known as “disk interleaving”, ” striping” or ” striping“, is also found in RAID 5 systems.
Because of this distribution principle, the storage capacity of a RAID 0 system corresponds to that of the smallest disk, multiplied by the number of disks in the array. While striping makes full use of all available storage space, excess storage space remains unused when disks of different capacities are used.
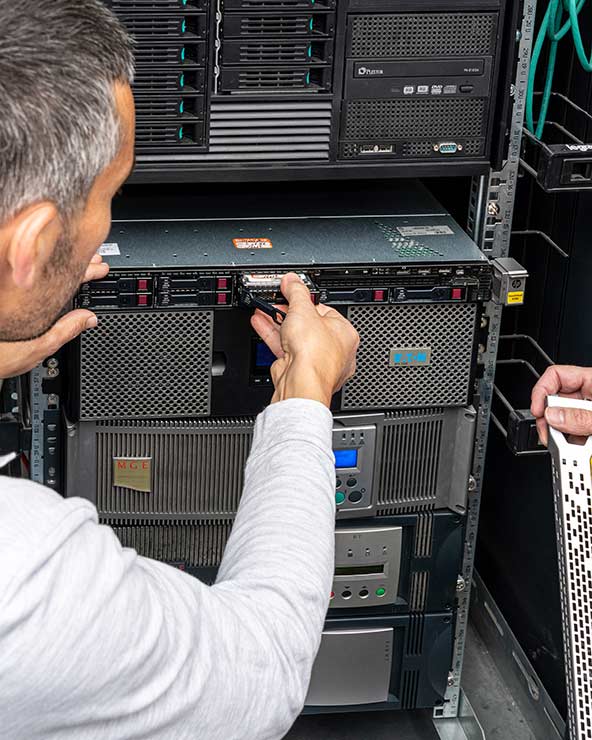
RAID 0 hard disks share their cache memory, distributing the workload both for reading and writing. During a write operation, for example, data is split into blocks distributed simultaneously across the different disks. Data access time and processing speed therefore improve considerably with the number of disks present.
The RAID 0 system is therefore perfectly suited to operations involving large amounts of data, requiring both fast and stable transfers. It is used for its high performance and bandwidth in the audiovisual sector, communication agencies, image processing, video and audio editing…